Internal jugular vein
CCA - common carotid artery
CN - cranial nerve(s)
EJV - external jugular vein
ICA - internal carotid artery
IJV - internal jugular vein
LIJ - left internal jugular vein
LN - lymph node
RIJ - right internal jugular vein
SCM - sternocleidomastoid muscle
SCV - subclavian vein
SVC - superior vena cava
Origin and course
- originates at superior jugular bulb in cranium (confluence of inferior petrosal sinus and sigmoid sinus)
- exits cranium via jugular foramen with cranial nerves 9-11, posterior to ICA
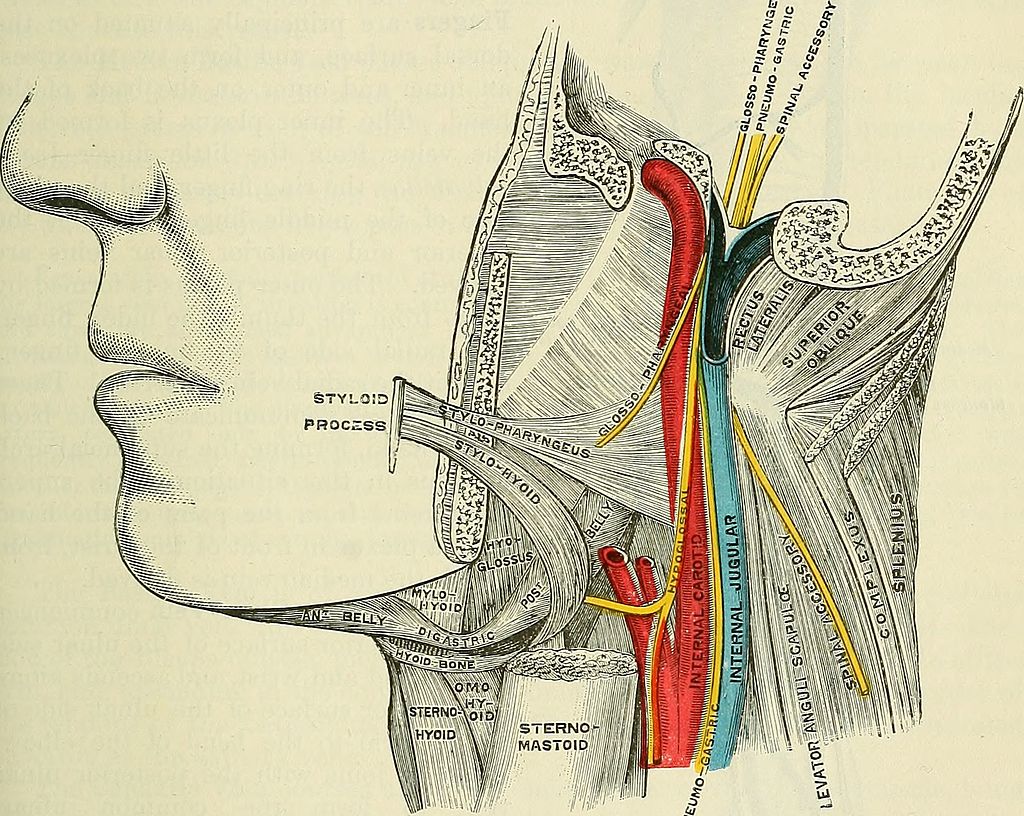
- descends laterally to ICA which is continuous with CCA in the carotid sheath
- moves anterior and lateral to CCA in anterior triangle of neck
- descends deep to SCM
- widens to form inferior jugular bulb posterior to medial clavicle where it joins SCV
- R) SCV → SVC
- L) SCV → innominate vein → SVC
- RIJ usually larger than LIJ
You may notice the IJV moves from posterior to anterolateral as you scan inferiorly down the neck when inserting a central line.
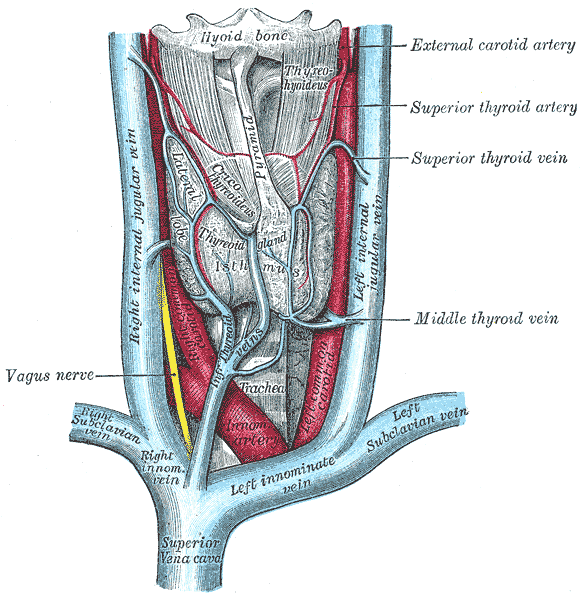
Tributaries
- facial, pharyngeal, lingual, sup/middle thyroid and occipital veins
Surface anatomy
The anterior neck triangle is formed by:
- mandible
- midline
- anterior/medial border of SCM
The IJV is 0.5-1cm lateral to the palpable carotid pulse at the apex of this triangle (near the sternum).
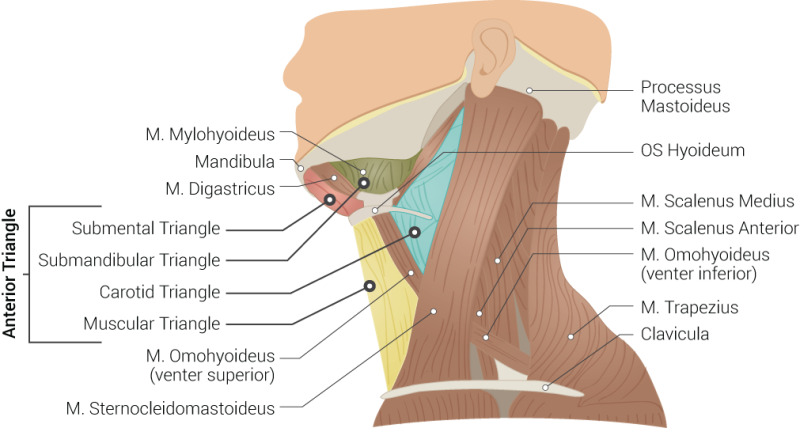
Muscles and triangles of neck by Beckie Palmer CC BY, via Anatomy Tool
Relations
Anterior
- superior neck - skin, subcutaneous tissue
- inferior neck - SCM
Posterior
- from superior to inferior:
- lateral mass of cervical vertebrae, scalene, pleura, sympathetic chain
Medial
- CCA as described
- CN 9-12 superiorly
- thyroid gland, trachea, oesophagus
Lateral
- SCM
- thoracic and right lymphatic ducts enter SCV just lateral to insertion of IJV
Inferior
- pleura (rises 2.5cm above clavicle)
In carotid sheath
- vagus nerve
Important structures
- vagus nerve travels between CCA and IJV in the carotid sheath
- cervical sympathetic plexus is posterior to the carotid sheath
- EJV is posterior, lateral, and superficial to IJV. It inserts into SCV
- the deep cervical LNs are in close proximity to IJV
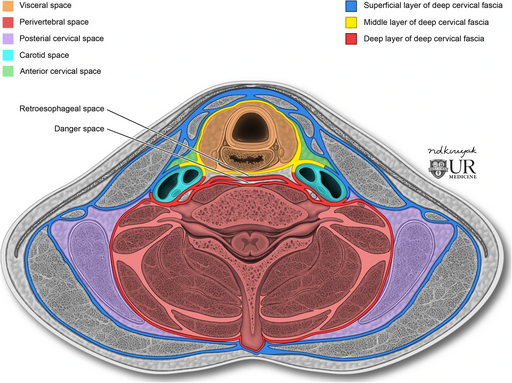
Infrahyoid deep neck spaces CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia
Anatomical variation
- duplication (bifurcation, with each limb joining SCV separately)
- fenestration (bifuration which reunites before joining SCV)

