Complement
Explain the role of complement
Mast cell and basophil degranulation
Antibody function / opsonisation
Chemotaxis
MAC - membrane attack complex
>25 plasma glycoproteins that are mostly made by the liver, the most important of which are C1-9. They are activated in cascade and serve as important signalling molecules with intrinsic antimicrobial activity.
Four main functions:
-
triggers basophil and mast cell degranulation
- → release of proinflammatory cytokines, prostaglandins, histamine, NCF, ECFA
- → increased vascular permeability, leucocyte migration and vasodilation
-
membrane attack complex (MAC)
- activated C5-9 form MAC, which perforate holes into bacteria → water influx and lysis
-
Opsonisation - bind to pathogens and act as antibodies,forming a binding site for for easier phagocytosis
-
Chemotaxis - acts as a signal to facilitate leucocyte migration to the area
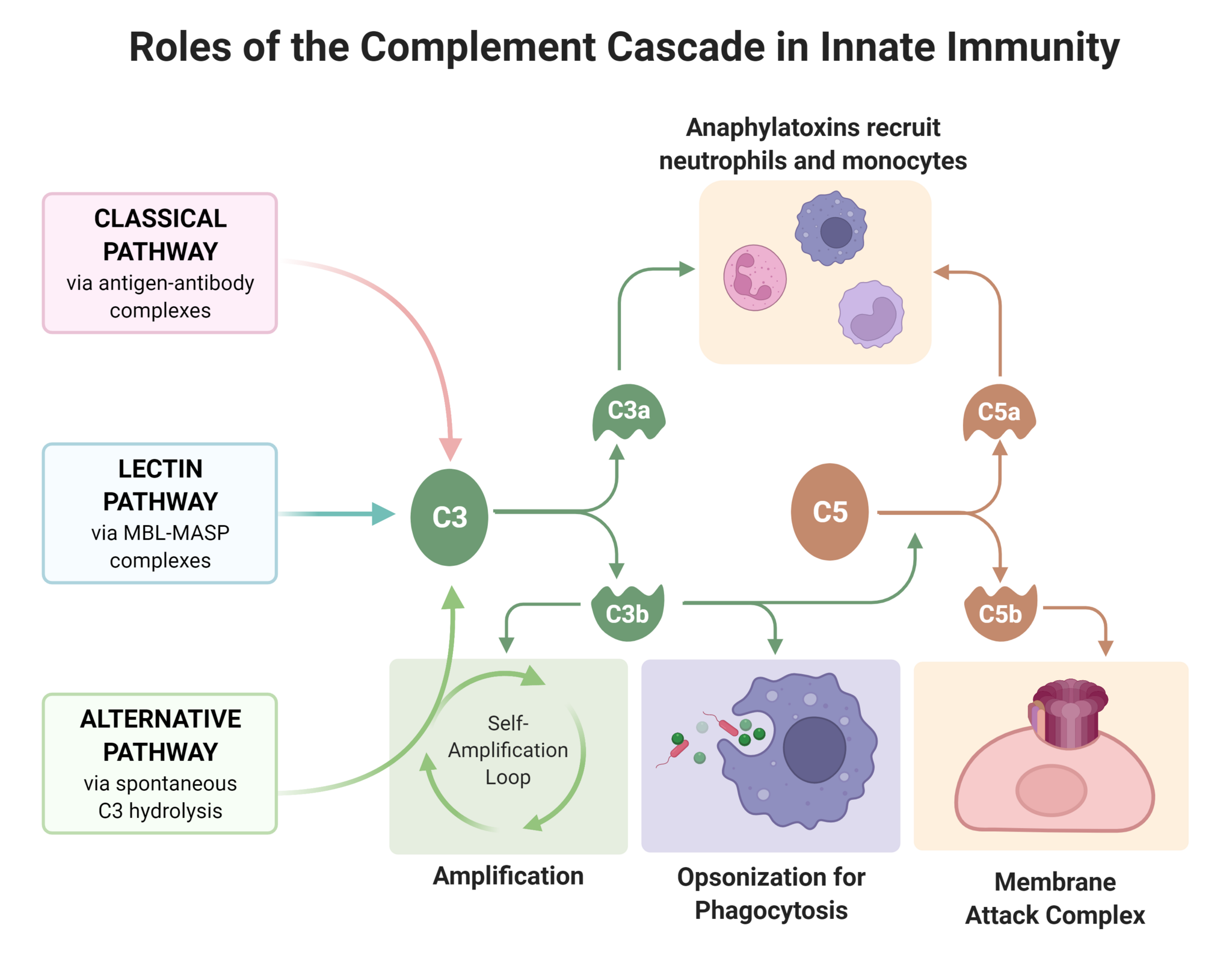
By סתו כסלו CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
Explain the activation of complement
Classical pathway
Activation
-
An antibody (e.g. IgM, IgG) binds to an antigen forming an immune complex.
-
The Fc portion of the antibody undergoes conformational change and binds to C1, activating it.
C3 convertase formation
-
Activated C1 cleaves C2 into C2a and C2b, and C4 into C4a and C4b.
-
C2a and C4b combine to form C4b2a which is a C3 convertase.
C3 and C5 cleavage
-
C3 convertase cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b.
-
C3b causes C5 to split into C5a and C5b.
Amplification
- C3b fragments catalyse further action of C3 convertase, generating more C3a and C3b
End functions
- C5b and C6-9 combine to form MAC
- The components not involved in MAC formation (C3a, C4a, C5a) are anaphylatoxins which trigger chemotaxis and mast cell degranulation
- C5b is an opsonin
Alternative pathway
- C3 binds directly to bacterial lipopolysaccharide membrane
- it interacts with factors P, B and D to become a C3 convertase, which acts in the same way as the classical pathway
Lectin pathway
- also known as the mannose-binding lectin pathway
- the mannose-binding lectin (MBL) complex is activated by carbohydrates only found on fungal and bacterial cell walls (e.g. mannose and mannan)
- the activated MBL cleaves C2 and C4, forming C3 convertase and joining the classical pathway
Regulation
- C1 esterase breaks down C1, regulating the activation of the classical pathway
- various proteins bind and inactivate C3 convertase e.g. Factor I
- protectin (a protein) prevents MAC from acting against host cells
- anaphylatoxins (C3a, C4a, C5a) are rapidly degraded in plasma before inflammatory effects can be spread elsewhere
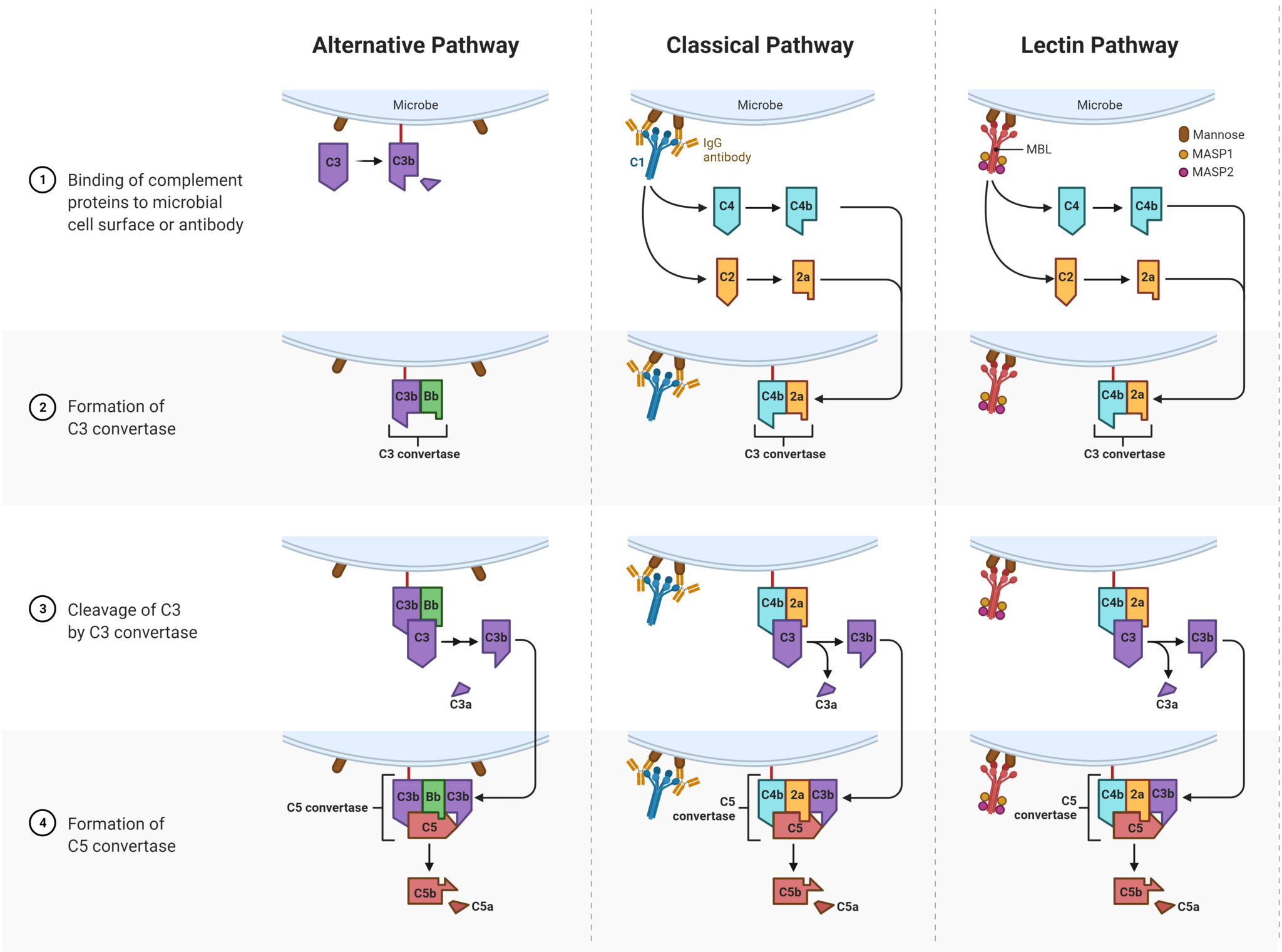
By סתו כסלו CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
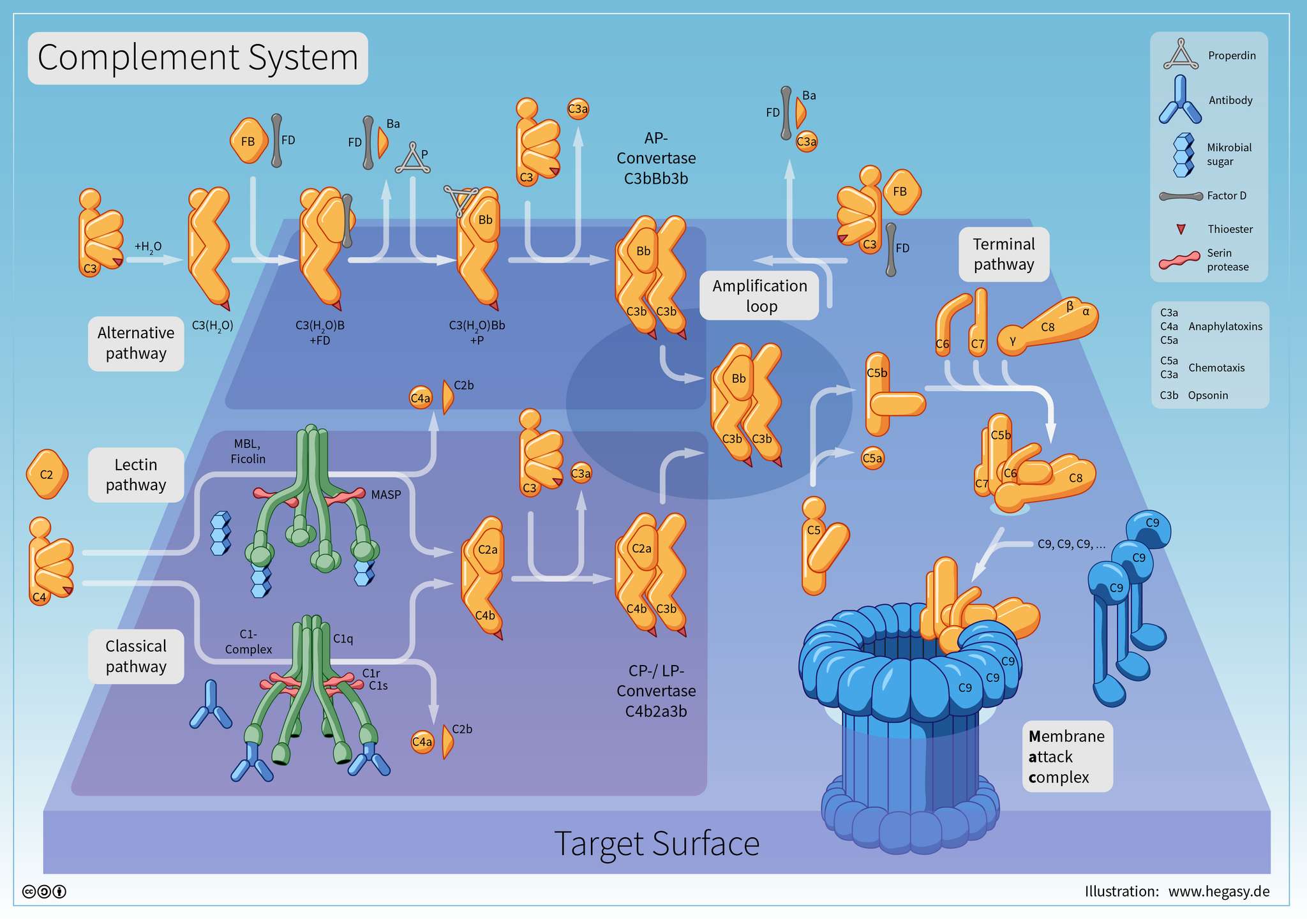
By Dr Hegasy CC BY-SA 4.0

