Subclavian vein
Origin and course
- continuation of the axillary vein where it crosses anteriorly to, and at the lateral border of, the first rib
- this occurs along the subclavian groove of the first rib
- the cephalic vein inserts into the axillary vein before it becomes the subclavian vein
- it crosses posterior to the clavicle at the midclavicular line
- it is anterior to the subclavian artery, separated by the anterior scalene muscle which inserts into 1st/2nd rib
- drainage into superior vena cava (SVC)
- the right subclavian vein drains directly into the SVC
- the left subclavian vein drains into the innomminate vein which crosses the midline and before draining into the SVC
- these occur posterior to the sternoclavicular joint at the medial border of anterior scalene
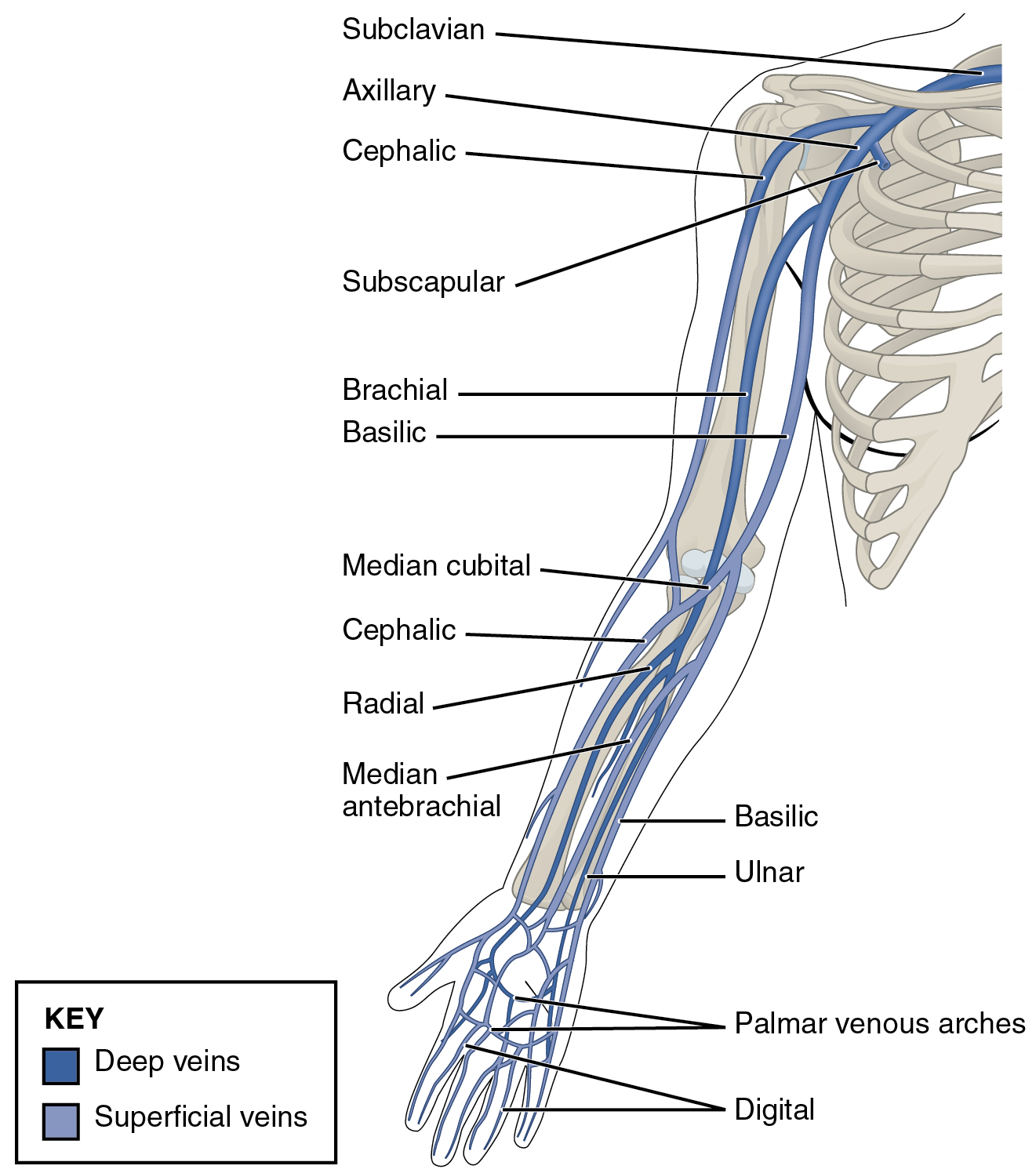
OpenStax AnatPhys fig.20.38 - Thoracic Upper Limb Veins CC BY 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
Tributaries
- external jugular vein
- lymphatic ducts
- the right lymphatic duct drains into the right subclavian vein
- it receives lymph from the right arm, right hemithorax, and right side of the head and neck; totalling 25% of total body lymph drainage
- the thoracic duct drains into the left subclavian vein
- it receives the lymph from the remaining 75% of the body
- the right lymphatic duct drains into the right subclavian vein
- dorsal scapular veins
- anterior jugular veins
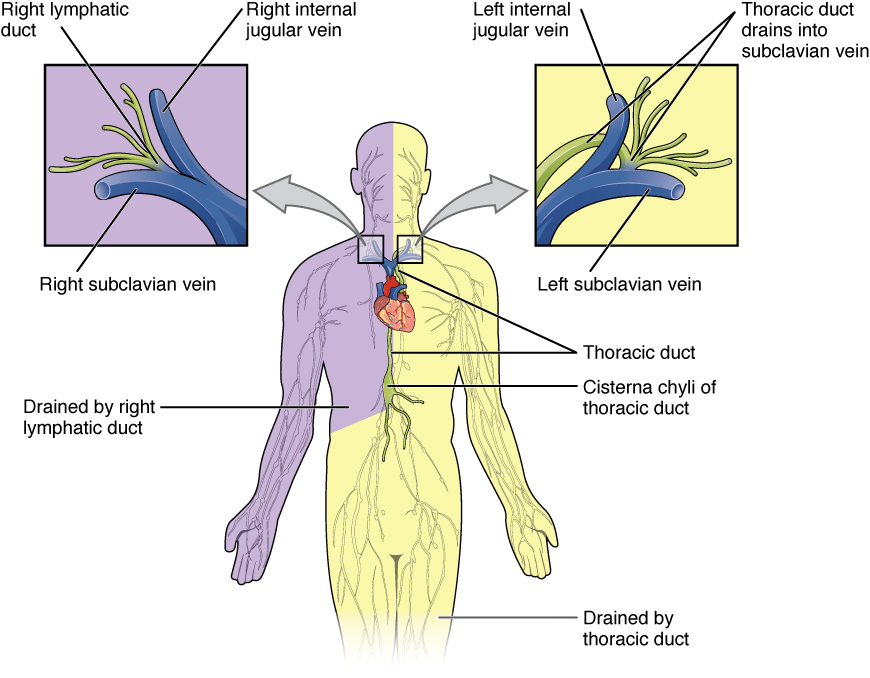
OpenStax AnatPhys fig.21.4 - Lymphatic Trunks and Ducts System CC BY 4.0
Relations
Anterior
- clavicle
- subclavius muscle
- pec major
Posterior
- subclavian artery (posterior and superior to vein)
- anterior scalene muscle
- 1st rib and intercostal space
- phrenic nerve
- lung apex and pleura
Superior
- subclavian artery (posterior and superior to vein)
- clavicle
- neck muscles and platysma
Medial
- trachea
- carotid sheath and its contents
Lateral
- axillary vein
- inferior trunk of brachial plexus
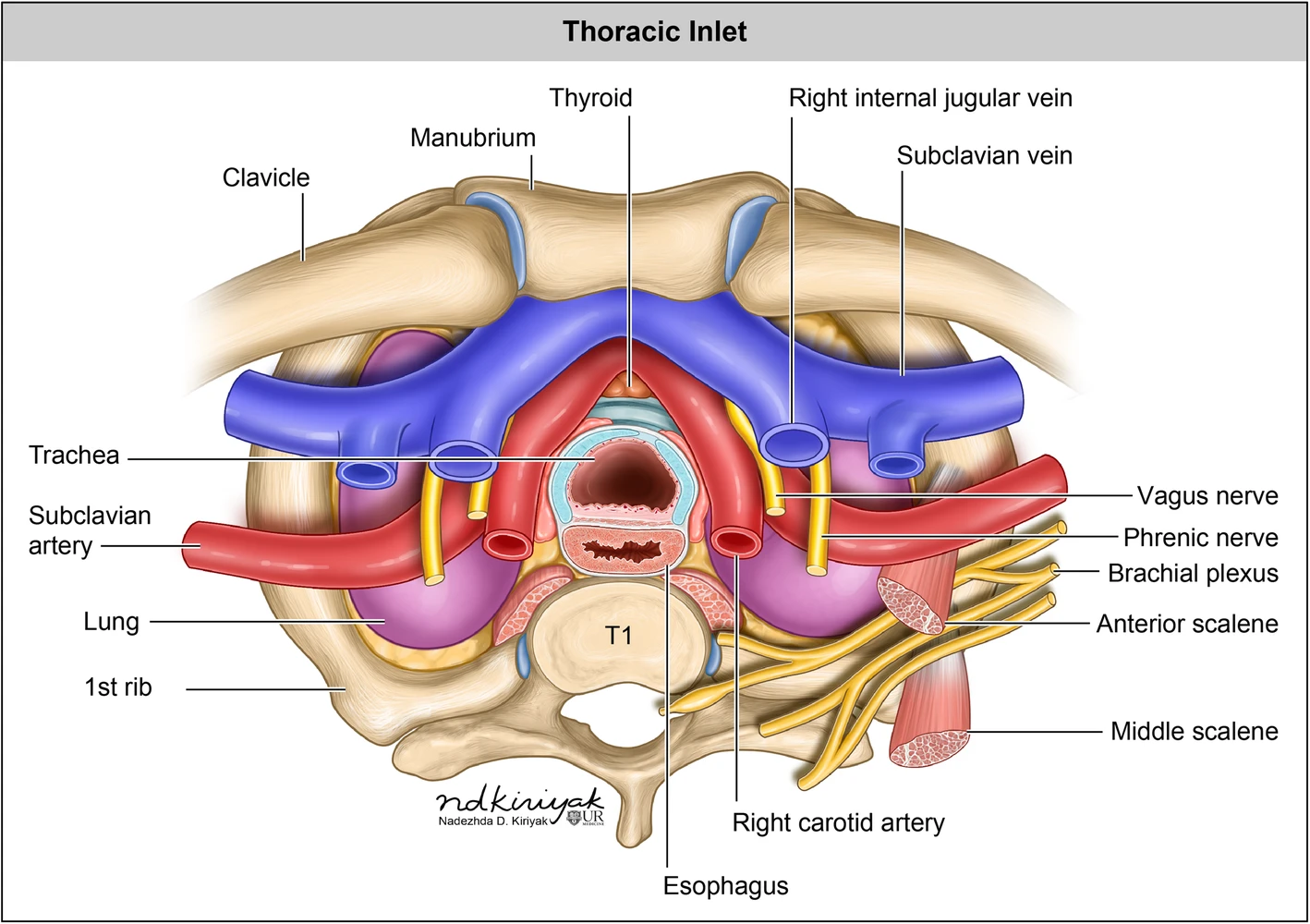
Anatomy of the thoracic inlet by Nadezdha D. Kiriyak CC BY 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
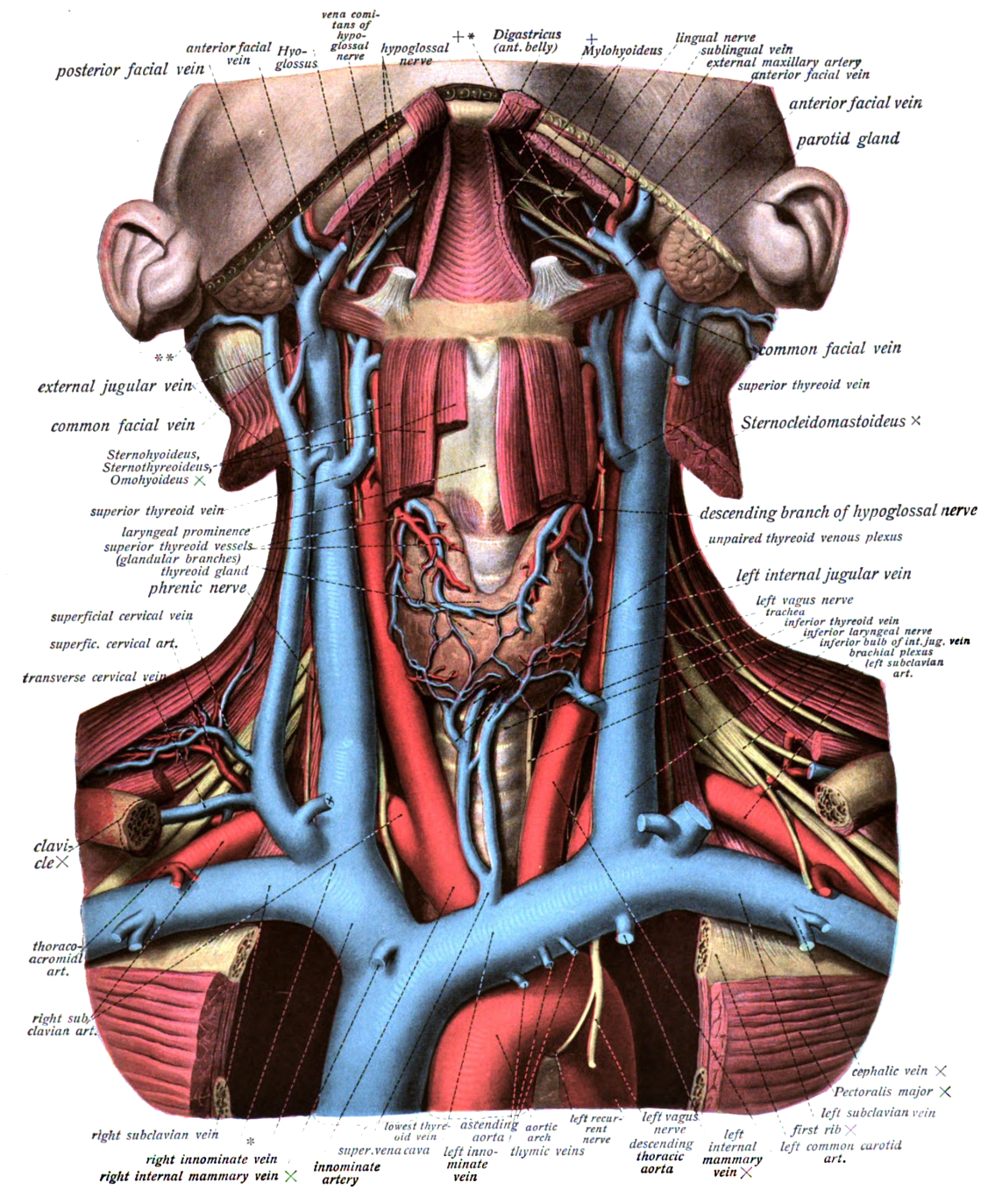
Surface anatomy
- the deltopectoral groove is palpated, found at the lateral third of the clavicle
- a needle directed towards the sternal notch, posterior to the clavicle, and with a shallow angle of attack will meet the subclavian vein where it crosses posterior to the clavicle at the midclavicular line
- the subclavian vein can also be cannulated using a supraclavicular approach
ON THIS PAGE

